In a physical, medical or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. A physical examination instrument is a medical equipment designed to aid in the diagnosis, monitoring or treatment of medical conditions. The various departments in a hospital setting use various medical equipment in relation to the function. Today, we are going to focus on the medical examination instruments found in a triage room. A triage room is a place where there is allocation of patients according to the urgency of their need for care. Just like an emergency room, it is a room for sorting of and allocation of treatment to patients and especially battle and disaster victims according to a system of priorities designed to maximize the number of survivors.
The triage room is where physical examination of patients takes place. There are usually hundreds or even more patients walking into a clinic daily. Most of them have no idea what the matter is and a nurse needs to carry out a physical examination to determine the patient's health condition for diagnosis.
So we're here to understand what these medical equipment are called as well as their functions. Next time you visit the hospital, be sure to do a quick brain on them and jog your memory.
Physical examinations are important for catching disorders and diseases before they affect a patient. They should be completed when the patient is healthy, so the physician has a baseline for the patient’s condition. When the patient is sick or suffering from a medical problem, the physician and medical assistant can use the medical examination instruments to check the health of the patient and understand the treatments that are needed to help them recover. During a clinical examination, the medical assistant will assist the physician. The medical assistant may check in the patient, escort the patient to the examination room, prepare the patient for the examination, manage the instruments and supplies for the physician, and help the patient after the exam scheduling any follow up appointments.
Inspection. This is considering clues from viewing the patient's skin, appearance, well being.
-When you look at the patient, you check the dress code in regards to the weather, the demeanor, and the body shape. Also the facial expression shows pain or otherwise among other observations.
Palpation. This is gathering information from what the practitioner feels by touching the patient such as feeling patient for a pulse.
-When a patient arrives, the medical assistant can shake hands at the beginning of the consultation to take notes. This can be for checking whether the hands are hot which indicates fever or cold to indicate peripheral vascular disease symptoms.
Percussion. This involves tapping on a surface and listening to different percussion notes to determine the makeup of underlying tissues.
-This technique uses sounds that give clues to indicates whether there's solid over bones, liquid/fluid over ascites or gas over chest cavity is present.
Auscultation. This is where a practitioner is listening to body parts including the heart or lungs using a stethoscope.
-The process varies for adults and infants mainly with the instruments but perform similar function.
Mensuration. Means of measurement such as vital signs.
Manipulation. Another method that uses a range of motion.
The physician primarily works with the physical examination instruments; however, the medical assistant must become familiar with their uses to assist the physician during a clinical examination. The nurse or medical assistant can also be responsible for disinfecting and sanitizing the instruments and preparing them for the physician before the next physical examination.
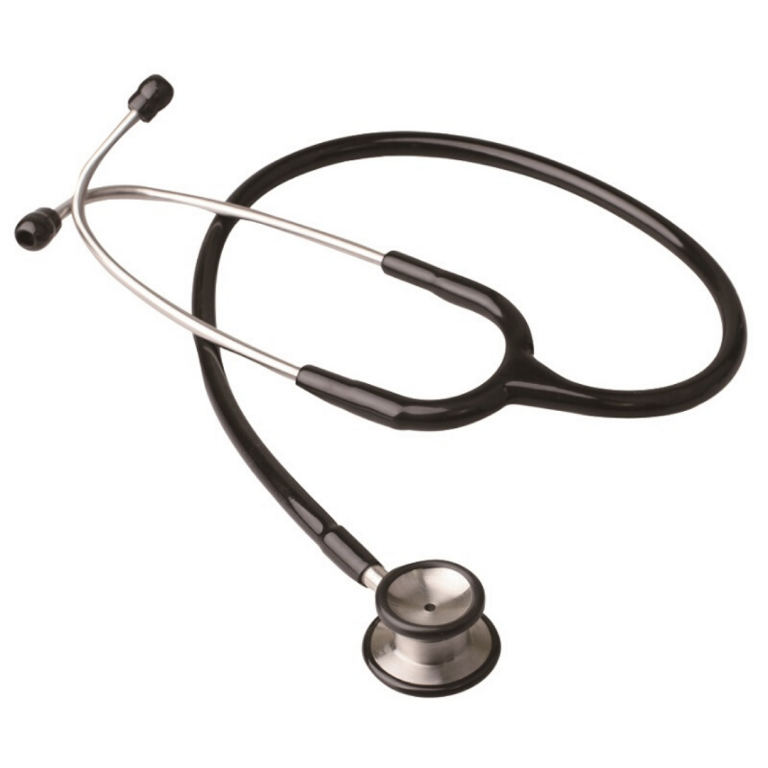
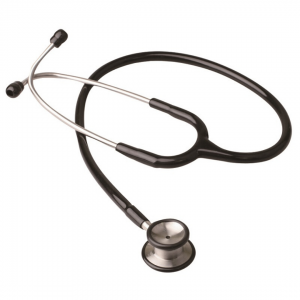
Stethoscope – used for listening to body sounds from movements within the body including the sounds of the heart, lungs and intestines. It is also used while taking blood pressure. You've probably seen a doctor with what looks like advanced Dr.Dre earphones hanging around the neck. Well, that's the stethoscope.
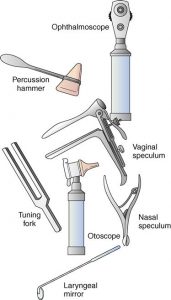
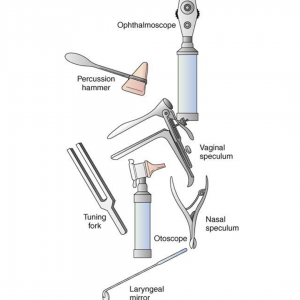
Ophthalmoscope – used to examine the interior structures of the eye. The ophthalmoscope has a light, magnifying lens and opening for the physician to view the eye.
Sphygmomanometer – It is used to measure a patient’s blood pressure. The sphygmomanometer is composed of an inflatable rubber cuff, a bulb that inflates and releases pressure from the cuff, and use of a stethoscope to listen to arterial blood flow in the patient.
Otoscope – allows the physician to view the ear canal and tympanic membrane. The otoscope has a magnifying lens, light and cone-shaped insert to examine the inner ear.
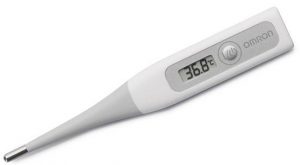
Patient Thermometer – instrument used to measure a patient’s body temperature. The thermometer can be inserted in the mouth under the tongue, under the armpit or into the rectum.
Suction Machine - a device used to suck up blood or secretions.
Nasal Speculum – inserted into the nostril to assist the physician with the visual inspection of the lining of the nose, nasal membranes and septum.
Audioscope – used to screen patients for hearing loss. The audioscope is placed in the patient’s ear and makes a serious of tones which the patient can respond to.
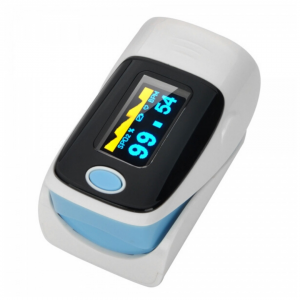
Pulse oximeter - used to measure the oxygen saturation level in the blood.
Examination Light – the medical assistant must make sure that all lights in the physical examination room are functioning properly and directed appropriately for the physician to exam the patient’s body.
Weighing Scale - used to measure the mass of patients. Can either be a baby scale or adult and these come in digital or manual specifications.
Manual Wheelchairs - a straight-back chair with wheels used as a mobility device for patients who have difficulty walking due to an injury or old age.
Fetal Doppler - this instrument is used for listening to the baby heartbeat in the womb.
Laryngeal Mirror – used to visualize and examine the larynx and other areas of the throat. The laryngeal mirror reflects the inside of the mouth and throat for the physical examination.
Penlight – provides additional light for the physician to examine a specific area of the patient’s body. The penlight is typically used to examine the eyes, nose and throat.
Percussion Hammer – used to test neurologic reflexes. The head of the instrument is used to test reflexes by striking the tendons of the ankle, knee, wrist and elbow.
Tuning Fork – used to test a patient’s hearing. The physician strikes the prongs causing them to vibrate and produce a humming sound. Then the prongs are placed next to the patient’s skull, near the ear, with the patient describing what they heard. The physician may order additional tests depending on the results of this hearing test.
Additional Supplies are needed for a general physical examination.
Gloves – worn by the medical assistant and physician to keep bodily fluids from being absorbed into the skin.
Disposable Needles – used to inject medicine, anesthetic or other fluids during a physical examination. Also used to extract blood from the patient for laboratory testing.
Gauze, Dressings and Bandages – used to cover up open wounds. Non-sterile pads can be used to cushion, clean or absorb areas that are at less risk of infection.
Specimen Containers – used to hold blood, urine and other bodily fluids during an examination for later laboratory testing.
Cotton Balls – used to stop bleeding from minor punctures after injections or while drawing a patient’s blood.
Disposable Syringes – added to a needle to extract blood or inject fluids during a physical examination.
Paper Tissue – helps keep exam chairs, tables and other areas hygienic. The paper tissue is replaced between each examination by the medical assistant.
Tongue Depressors – used to depress the tongue of a patient to examine the mouth and throat during a physical examination.
Cotton-Tipped Applicators – used to collect or treat a wound and to apply topical medication to the patient during a physical examination.
These clinical examination instruments and more are available in our stores and can be ordered via our online platform.
Medical or clinical examinations are vital for diagnosing disorders and diseases before they affect a patient. A physical examination should be done when the patient is healthy, so that a physician has a baseline for the patient’s condition. When the patient is sick or suffering from a medical problem, medical assistant can use the examination instruments to check the health of the patient and diagnose treatments that will assist in curing or healing.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK361/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Physical_examination
Share with us your thoughts on the comment section below.
GM Medical, We got you covered!