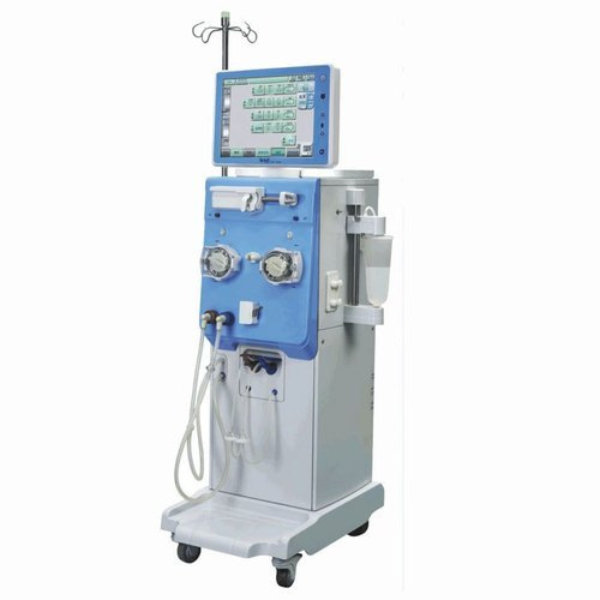
A dialysis machine is a device that mixes and monitors the dialysate which is a fluid that assists in removing waste products from your blood. During haemodialysis, which is a treatment of purifying blood by filtering waste and water from a person’s kidneys, the dialysis machine is able to remove blood through a dialyzer.
The dialyzer acts as an artificial kidney by filtering blood then returning the purified blood back to your body. It also monitors the movement of your blood outside your body during the process.
The haemodialysis takes between 3 to 5 hours and happens in a dialysis centre or in a hospital at least 3 times a week.
In 1943 Willem J. Kolff, a Dutch physician, developed a machine that cleans blood by acting as an artificial kidney. In 1950s, more experiments followed and led to the production of better designs of the dialysis machine. One disadvantage was that they could only treat acute kidney failure and not the end stage renal disease. In 1962, Dr. Belding Scribner, a medical professor, opened the first dialysis clinic in the USA. He developed a portable dialysis machine so that the people could receive treatment at home. To date, more than 90% of dialysis patients receive this treatment in dialysis centres.

Dialysis machine invented by Kolff
This process involves surgery for implanting a PD catheter into your abdomen. The peritoneal dialysis catheter enables blood to be purified by filtering and absorbing waste through a dialysate then draws waste from the blood.
This process uses an artificial kidney
This therapy process is used in ICU for patients with acute kidney failure and the machine that purifies the blood is used on a daily basis for treatment.
Today we focus on haemodialysis.
A blood tubing is used to carry blood and prevent it from mixing with the dialysate. This helps movement of blood by pumping it through the dialyser and back into your body.
These drugs are used to hold the liquid that mixes the dialysate made up of acidified solution bicarbonate and purified water. During the process the dialysate and purified water flow through your blood separately In the dialyzer, unwanted waste is removed from this blood into the dialysis then excreted and washed.
As the blood is moving in and out of the body, it might clot in the tubing. A treatment known as heparin is drawn up through the syringe into the pump to prevent the blood from clotting.
The dialysis machine monitors the pressure levels and lets you know when the blood pressure is too high or too low. It also checks the temperature levels, the blood flow and mixture of the dialysate. In case any of these goes off the grid, it will sound the alarm or shut down the blood flow and even let us know by blinking lights. In addition to that, the alarm will go off when it's done with the process.
There are two air traps inside the blood tubing. One will go before the dialyzer and another one after. The traps catch air that gets into the tubing to prevent any problems with the machine. However, in case the air gets into the blood pump, the blood flow is stopped until all the air is taken out.
Due to a limited number of kidney donors CKD patients mostly rely on the dialysis machine. There are a few side effects depending on the period of the dialysis therapy. Some short term side effects include; vomiting, convulsion, low blood pressure, stress, or tiredness. Long term effects include; cardiac insufficiency hypertension, carpal tunnel syndrome, or hyperkalaemia.
At GM Medical, we supply dialysis machines to medical centres for treatment on pre-order basis.
For more information regarding dialysis machines, please reach us on our email [email protected] or call +254722932625
https://wiki.ucl.ac.uk/display/BECS/Kidney+Dialysis#KidneyDialysis-SideEffectsandComplications
http://www.kidneydialysis.org.uk/inventor-of-dialysis.html